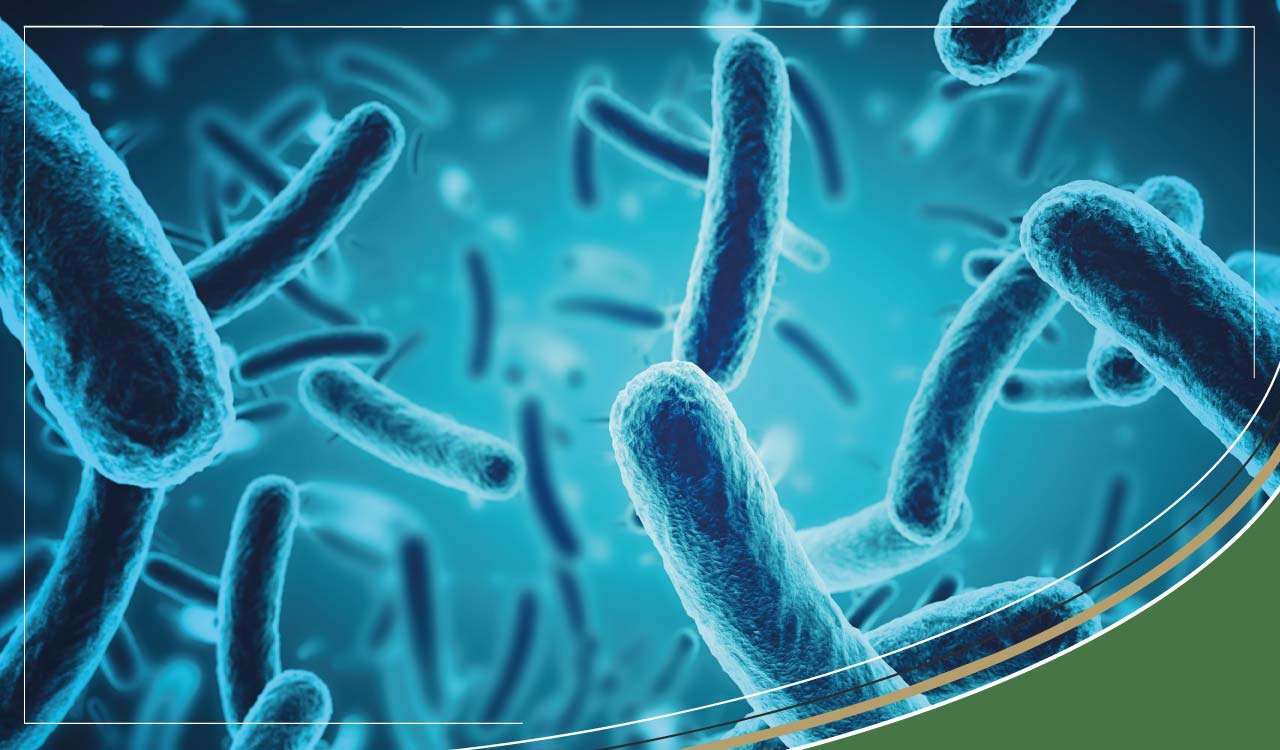
What is Streptococcus?
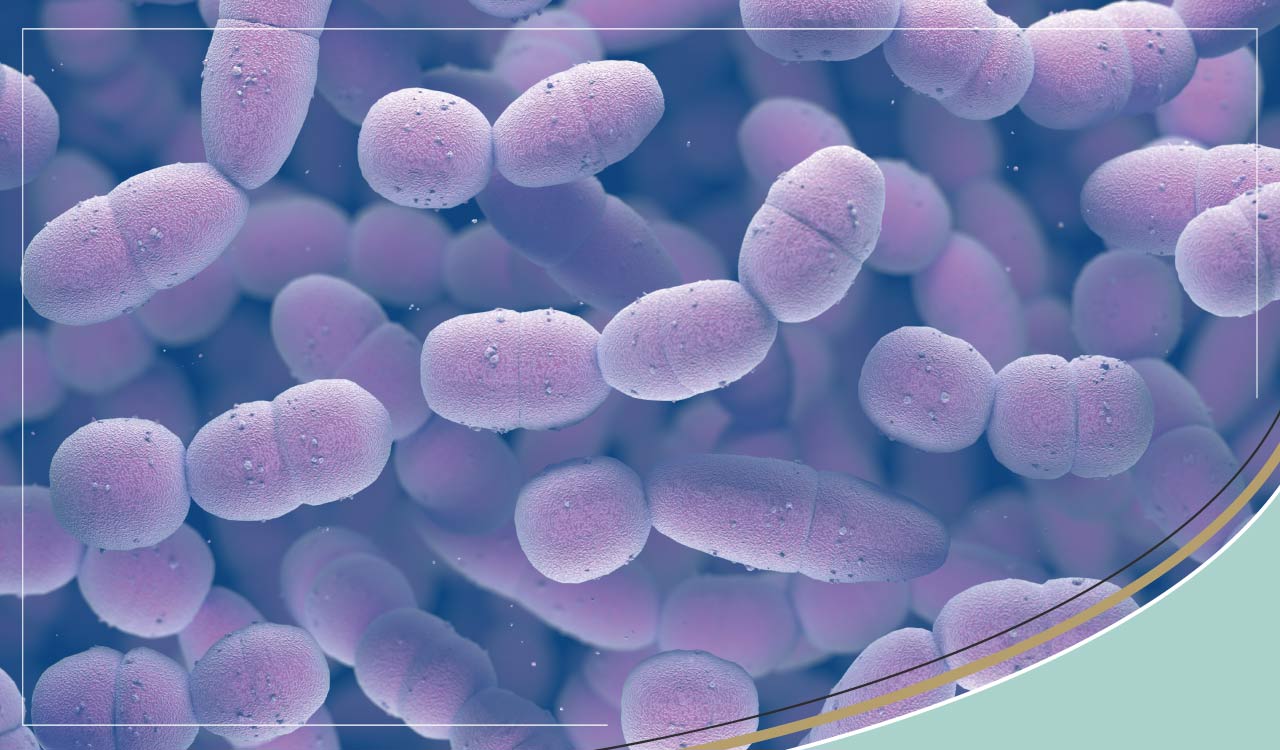
What is Streptococcus?
Streptococcus is a type of bacteria. When streptococci multiply, they grow in chains. They get their name from “streptos” which is Greek for 'twisted chain'.
Streptococcus is a gram-positive bacterium, unlike E-coli, which is gram-negative. Gram-positive bacteria give a positive result to the Gram Test - a way of staining bacteria so that they show up under a microscope. They retain the purple colour of the stain because they have a thick layer around their outer wall which holds in colour. Gram-bacteria have a more porous cell wall, so the colour leaks out.
There are very many different species of streptococcus, so they have been classified into various groups depending on their characteristics. Those that are most important to human health; Group A, B or D Streptococcus. There are also Group C, F, G and H types of Streptococcus, but these are more commonly found in animals such as horses, pigs and cattle, and are much less likely to cause infections in humans.
Streptococcus
Different species of streptococcus are responsible for a wide range of health conditions, ranging from mild to life-threatening. Some of the more common species and the conditions they can cause are listed below:
- Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A) -strep throat/pharyngitis, impetigo, scarlet fever, toxic shock syndrome
- Streptococcus pneumoniae (Group A)- bacterial pneumonia, sinusitis, meningitis
- Streptococcus agalactiae (Group B) - pneumonia and meningitis (in babies and the elderly)
- Streptococcus mutans (Group D) - tooth decay
- Streptococcus Bovis (Group D) -urinary tract infection, endocarditis
You should always seek medical advice if you suspect a streptococcal infection.
 Fast Delivery - 1-5 Working Days
Fast Delivery - 1-5 Working Days
 Free Delivery for all orders to France
Free Delivery for all orders to France
 Read Thousands of Independent Reviews
Read Thousands of Independent Reviews